Table of Contents
Introduction
Hand cream works only when its ingredients, texture, and usage match your skin barrier damage, climate, and hand-washing habits—not when you simply buy the most popular brand.
Dry, rough, aging hands are not just a cosmetic annoyance—they are a sign of repeated barrier damage. Frequent washing, sanitizers, weather exposure, and friction strip away lipids faster than your skin can replace them. Most people respond by buying random hand creams, then wonder why nothing changes. The solution is not more product—it’s the right formula used correctly.
Key Takeaways
Dry hands signal barrier breakdown, not lack of water
Climate and job determine the best hand cream texture
Occlusives lock in repair; humectants alone are not enough
Expensive brands don’t guarantee better outcomes
The best hand cream differs by country and environment
Hand cream is a concentrated topical product designed to repair, protect, and restore the skin barrier on the hands. Compared to body lotion, it contains:
Higher lipid content
Stronger occlusives
Longer-lasting film formers
Hands have fewer oil glands and are exposed constantly. That’s why face-grade hydration logic does not work here.
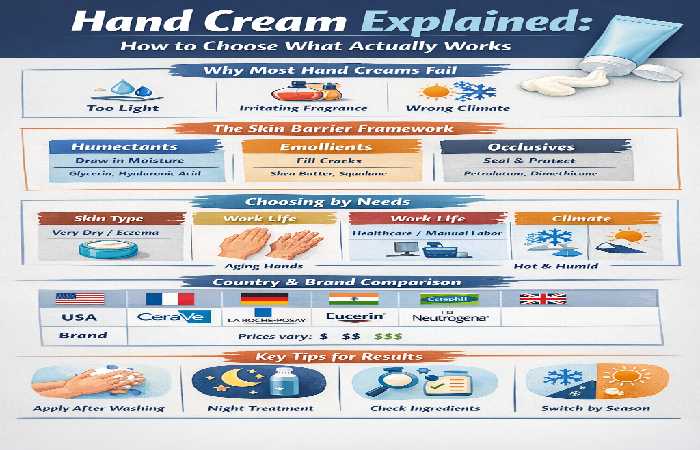
Why Most Hand Creams Fail
Most failures come down to mismatch.
Too light: absorbs fast but evaporates quickly
Too fragranced: worsens irritation
Wrong climate: thick creams in humidity feel sticky; gels in winter do nothing
Example:
A nurse washing hands 40+ times a day needs barrier sealants, not aloe-based hydration.
The Skin-Barrier Framework (How to Choose Correctly)
Every effective hand cream balances three components:
| Component | Role | Common Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Humectants | Pull water into skin | Glycerin, urea |
| Emollients | Smooth cracks | Shea butter, squalane |
| Occlusives | Lock everything in | Petrolatum, dimethicone |
If your hands crack or sting → you need occlusives.
If they feel tight but intact → emollients + humectants may be enough.
Choosing Hand Cream by Real-World Use
By Skin Condition
Extremely dry / eczema-prone: fragrance-free, petrolatum-based
Aging hands: niacinamide, ceramides, antioxidants
Sensitive skin: minimal formulas, no essential oils
By Profession
Healthcare workers: barrier creams with silicone polymers
Manual labor: thick balms with waxes
Office workers: fast-absorbing creams for frequent re-application
By Climate
Cold & dry (US, UK, Germany): heavy occlusives
Hot & humid (India, SEA): lighter emulsions, still barrier-focused
Competitive Comparison: Countries, Brands & Pricing
Specialist-Reviewed Hand Cream Comparison
| Country | Brand | Specialist Notes | Approx. Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | CeraVe | Barrier repair, ceramides | $$ |
| France | La Roche-Posay | Eczema-safe formulas | $$$ |
| Germany | Eucerin | Urea-based repair | $$ |
| India | Cetaphil | Sensitive-skin focus | $ |
| UK | Neutrogena | Glycerin-rich classics | $$ |
Pricing Insight:
Higher prices usually reflect dermatology testing and ingredient stability—not magical performance.
Ingredient Red Flags & Marketing Myths
“Non-greasy” often means under-occlusive
“Natural only” ≠ safer for damaged skin
Essential oils frequently worsen micro-cracks
Dermatology bodies like the American Academy of Dermatology and British Association of Dermatologists consistently prioritize barrier integrity over sensory appeal.
How to Use Hand Cream for Results
Apply after every wash, not just at night
Use a thicker layer before sleep
Pair with gentle, low-pH hand cleansers
Reassess seasonally
(Internal link hook: Deep guide on repairing the skin barrier)
Trust & Expertise
This guide is built using:
Cosmetic ingredient science
Dermatology association guidelines
Comparative product analysis across climates
Real-world failure patterns observed in clinical skincare use
FAQs
1. Is hand cream necessary if I already use body lotion?
Yes. Body lotions are usually too light to protect the hand barrier from repeated washing and friction.
2. How often should I apply hand cream?
Ideally after every hand wash, especially if you use soap or sanitizer frequently.
3. What’s the best hand cream for very dry, cracked hands?
Formulas with petrolatum, dimethicone, or ceramides work best for repairing severe barrier damage.
4. Are expensive hand creams better?
Not always. Ingredient composition matters more than brand prestige.
5. Can hand cream help with aging hands?
Yes. Ingredients like niacinamide and antioxidants improve texture and tone over time.
6. Is hand cream safe for eczema-prone skin?
Yes, if it is fragrance-free and dermatologist-tested.
7. Which hand cream works best in hot climates?
Light creams with barrier-supporting ingredients that don’t rely only on water.
8. Can I use hand cream on cuticles and nails?
Absolutely. It helps reduce hangnails and nail brittleness.
9. Should I switch hand creams seasonally?
Yes. Winter and summer require different occlusion levels.